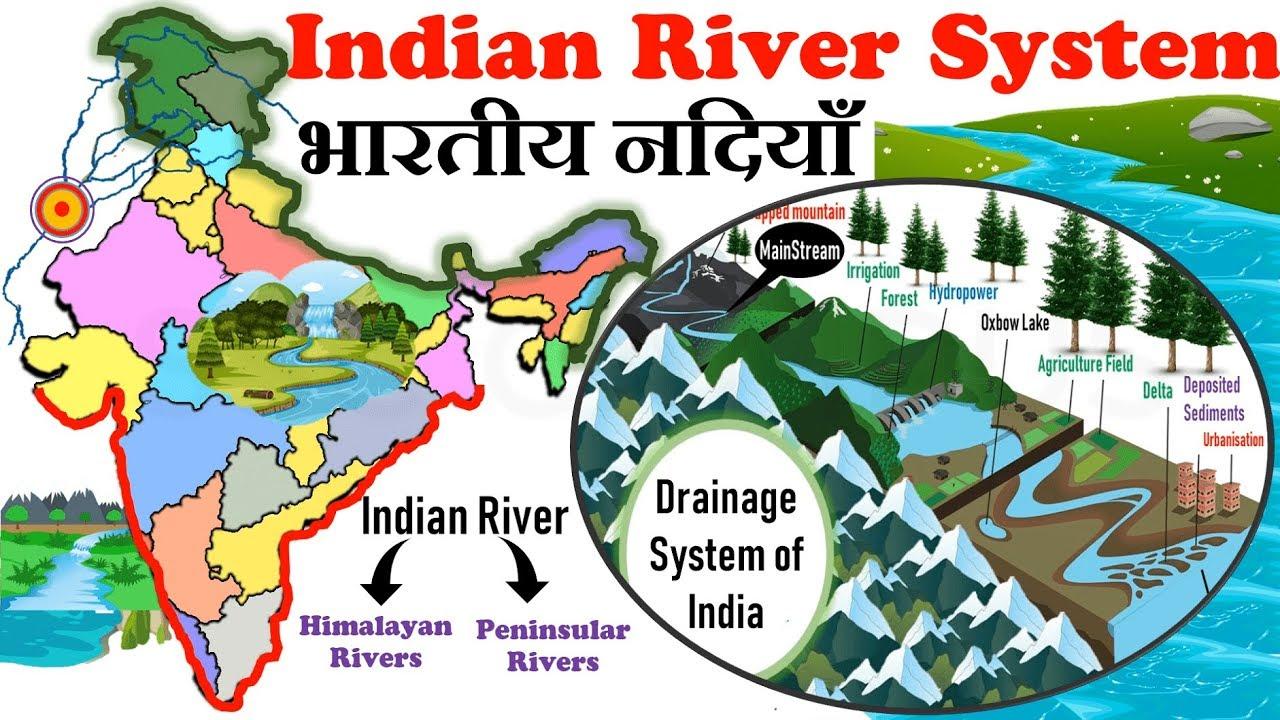
90 percent of India’s total surface water flowed into the Bay of Bengal and the rest is in the Arabian Sea. The drainage system flowing into the Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal is separated by a water divide along the Western Ghats, the Aravalli, and the Yamuna Sutlej. There are a large number of small and large rivers in the Indian drainage system. It is the result of the development process of the three major physical units and the nature and characteristics of rainfall.
The Himalayan rivers come from the Himalayas and flow through the Northern Plains.
Himalayan Rivers System:
- The Indus River System
- The Ganga River System
- The Yamuna River System
- The Brahmaputra River System
The main source of the Peninsular River System or Peninsular Drainage is the Western Ghats. Because the Western Ghats are forming a ‘ water divide, ‘ these rivers either flow eastward into Bengal Bay or westward into the Arab Sea. Peninsular rivers are rivers that are essentially rain-fed.
Peninsular River System:
- Mahanadi
- Godavari
- Krishna
- Cauvery
Drain into the Bay of Bengal as they flow on the plateau eastward and create a ‘delta’ at their mouths; while the Narmada Tapti-the west-flowing rivers fall into the Arab Sea and create’ estuaries.’
Not from glaciers, but from rain-fed rivers. During summer, these rivers significantly decrease or dry up.

HIMALAYAN Drainage System
Indus River System
In the early Hindu mythological texts, the mention of the Indus River or Sindhu River is witnessed. The river comes from Tibet near Lake Mansarovar. In Jammu and Kashmir, it flows westward into India, flows further through Himachal Pradesh, and Punjab, and reaches Pakistan.
It enters the Arab Sea near Karachi, flowing further west. Indus is Pakistan’s biggest river and the national river of the country. Its Indian tributaries are Zanskar, Nubra, Shyok, and Pakistan’s Hunza. Sutlej, Ravi, Beas, Chenab and Jhelum are their other tributaries named after the state of Punjab.

Ganga River System
The Ganga river system (Ganges) is India’s largest Drainage system. It originates in the glaciers of Gangotri. The upstream Bhagirathi joins the other stream at Devprayag called Alaknanda to form the Ganga River. Ganga has tributaries on both banks; the Yamuna and Son are its right-bank tributaries.
Some of the left bank tributaries are Gomti, Ghaghara, Gandak, Kosi. The Ganges flows through the Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, and West Bengal Indian countries. It lastly reaches the Bay of Bengal.
Yamuna River System
The Yamuna is Northern India’s main river system. The river flows through Uttrakhand, Uttar Pradesh and Haryana from Yamnotri. It crosses Delhi, Mathura, Agra and meets the Chambal, Betwa and Ken rivers to lastly join the Allahabad Ganga. Tons, Chambal, Hindon, Betwa and Ken are Yamuna’s major tributaries.
Brahmaputra River System
The Brahmaputra, one of India’s main rivers, originates in Tibet’s Himalayan Angsi glacier. It’s called the Tsangpo River there. In Arunachal Pradesh, it enters India and is known as Dihang River.
Dibang, the Lohit, the Kenula are tributaries which form the primary Brahmaputra River and flow through Assam, its longest course, enter Bangladesh and lastly falls into the Bay of Bengal. The Brahmaputra has the largest water quantity of all India’s rivers.

Important Drainage System of HIMALAYAN India
| RIVER | SOURCE | MOUTH | TRIBUTARIES | DESCRIPTION |
| INDUS | Near Bokhar Chu Glacier, Tibetan Plateau | Arabian Sea (near Karachi, Pakistan) | Left: Jhelum, Chenab, Sutlej, Ravi, Beas, Zanskar Right: Shyok, Hunza, Gilgit, Kabul, Khurram, Tochi, Gomal, Viboa, Sangar | Known as Singi Khamban (Lion’s Mouth) In India, it flows only in Jammu & Kashmir state |
| JHELUM | Verinag, J & K | R. Chenab (in Pakistan) | Right: Neelum, Sind | It passes through Srinagar and Wular Lake |
| CHENAB | Tandi, Himachal Pradesh (formed by two rivers Chandra and Bhaga) | R. Indus (in Pakistan) | Right: Marusadar river | It is also called as Chandrabhaga It is the largest tributary of river Indus |
| RAVI | Rohtang Pass, Himachal Pradesh | R. Chenab | ||
| SUTLEJ | Raksas Tal, near Mansarovar, Tibet | R. Chenab, Pakistan | Left: Baspa Right: Spiti, Beas | It is known as Langchen Khambab in its source place. It enters India through Shipki La pass Bhakra Nangal Project is constructed across this river |
| BEAS | Beas Kund, near Rohtang pass, Himachal Pradesh | R. Sutlej | ||
| GANGA | Confluence of R. Bhagirathi and R. Alaknanda at DevPrayag | Sagar Island, Bay of Bengal (Bangladesh) | Left: Ramganga, Gomati, Gandak, Kosi, Ghaghara, Mahananda Right: Yamuna, Son, Chambal, Betwa | Ganga is India’s largest river system |
| YAMUNA | Yamunotri Glacier | R. Ganga, Allahabad (UP) | Left: Rishiganga Right: Chambal, Betwa, Ken, Sind | It is the longest tributary of Ganga river |
| CHAMBAL | Mhow, Malwa plateau | R. Yamuna, Madhya Pradesh | Left: Banas Right: Parbati, Shipra | Badland topography is an important feature of the Chambal river system |
| GANDAK | Mustang, Nepal | R. Ganga, Sonpur, Bihar | Left: Trisuli Right: Kali Gandak | |
| GHAGHARA | Mapchachungo, Tibet | R. Ganga, Bihar | Left: Rapti Right: Sarda, Budhi Ganga | |
| KOSI | Tribenighat, Nepal | R. Ganga, Bihar | It is an antecedent trans-boundary river | |
| RAMGANGA | Pauri Garhwal, Uttarakhand | R. Ganga, Uttar Pradesh | ||
| SON | Amarkantak Plateau | R. Ganga, Bihar (near Patna) | It flows northwards to reach Ganga and its largest south bank tributary | |
| MAHANANDA | Darjeeling Hills | R. Ganga, West Bengal | Last left bank tributary of Ganga |
PENINSULAR Drainage System
Mahanadi
The Mahanadi in East-central India is a significant river. It originates in Chhattisgarh’s Sihava hills and flows through the state of Orissa (Odisha) through its main course. This river deposits more silt on the Indian subcontinent than any other river. Mahanadi runs through Sambalpur, Cuttack and Banki cities.
Godavari
The Godavari River, after the Ganga, covers India’s second-longest course. The river originates from Triambakeshwar in Maharashtra and flows along with its tributaries (Pravara, Indravati, Maner Sabri etc.) through the countries of Maharashtra, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, Orissa (Odisha), Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka and Puducherry to lastly flow into the Bay of Bengal. The river is defined as Dakshina Ganga because of its lengthy course.
Krishna River
The Krishna is India’s third-longest river, about 1300 km long. It originates from the Mahabaleshwar region of Maharashtra and flows through Karnataka, Telangana, and Andhra Pradesh to lastly pour into Bengal Bay.
Kaveri River
The Kaveri (Cauvery) is a significant river in southern India and originates in Kogadu, Karnataka.
As many tributaries like Hemavati, Moyari, Shimsha, Arkavati, Honnuhole, Kabini, Bhavani, Noyill and Amaravati join it, Kaveri River expands.
Narmada and Tapti
The Narmada & Tapti river is the only major flowing rivers into the Arab Sea. Narmada’s complete length flowing through Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, and Gujarat countries is equal to 1312 km. Amarkantak is Narmada’s location of origin in Shahdol, Madhya Pradesh. From east to west, Narmada flows primarily through Central India and flows into the Arabian Sea.
The Tapti river follows a parallel course to the south of Narmada, flowing through the Maharashtra and Gujarat states on their way into the Gulf of Khambat. Purna, Girna and Panjhra are its three main tributaries.
Like most ancient religions, rivers are considered sacred by the Hindu faith and its mythology. The Ganges, Yamuna (a Ganges tributary), Brahmaputra, Mahanadi, Narmada, Godavari, Tapi, Krishna, and Kaveri are nine major Indian rivers. Indian soil also flows through parts of the Indus River.
The Drainage System of India comprises eight important rivers together with their various tributaries. Most rivers discharge their waters into the Bay of Bengal; nevertheless, there are a number of rivers whose itineraries take them across the west end of India and into the Arab Sea in the east direction.
Northern parts of the Aravalli range, Ladakh parts, and the barren Thar Desert regions have Inland Drainage.

Important Drainage System of PENINSULAR India
| PENINSULAR RIVER | SOURCE | MOUTH | TRIBUTARIES | DESCRIPTION |
| MAHANADI | Sihawa, Chattisgarh | Bay of Bengal (False Point, Odisha) | Left: Seonath, Mand, Ib Right: Ong, Jonk, Telen | Maharashtra, Chattisgarh, Jharkhand, and Odisha are its basin states |
| GODAVARI | Brahmagiri Hills, Nasik, Maharashtra | Bay of Bengal, Andhra Pradesh (East Godavari district) | Left: Prahnita, Indravati Right: Manjira, Pravara, Manair | It is called Dakshin Ganga as this river is the largest Peninsular River |
| KRISHNA | Mahabaleshwar, Maharashtra | Krishna district, Andhra Pradesh, Bay of Bengal | Left: Bhima, Musi, Munneru Right: Tungabhadra, Koyna, Dudhganga, Ghataprabha | |
| CAUVERY | Brahmagiri Hills, Karnataka | Poompuhar, Tamil Nadu, Bay of Bengal | Left: Hemavathi, Arkavathy Right: Kabini, Bhavani, Noyyal, Amaravati | This river receives rainfall from both south-west and north-east monsoon |
| NARMADA | Amarkantak Hills, Madhya Pradesh | Gulf of Khambat, Arabian Sea | Left: Tawa, Shakkar Right: Hiran, Kolar, Dindori | Known for Marble Rocks (Jabalpur, MP), and falls West flowing river and flows through a rift valley |
| TAPI | Betul District, Madhya Pradesh | Gulf of Khambat, Surat, Arabian Sea | West flowing river |
.
Read More Articles on Geography
You Can Follow on Youtube – Score Better
Join Us on Telegram For More Update
.
Kindly provide Your valuable feedback