All permafrost thaw leads to greenhouse gas emissions. But standing water accelerates the threat. The gas that bubbles from the oxygen-deprived mud under ponds and lakes is not only carbon dioxide but also methane, which is 25 times as potent a greenhouse gas as CO2.
What is permafrost?
Any ground that remains completely frozen (0°C) or below for at least two years is called permafrost. It is formed of a combination of soil, rocks and sand that are held together by ice.
These permanently frozen grounds are usually situated in regions with high mountains and in Earth’s higher latitudes near the North and South Poles.

Geographic Distribution
At higher latitude, they are found in Canada, Alaska in the USA, the Siberian region in Russia and Antarctica. In northern Siberia, its forms are around 1,500 m deep and in northern Alaska, 740 m.
At lower latitude, it is found at high altitude locations such as the Alps and the Indian Himalayan Region, Tibetan plateau.
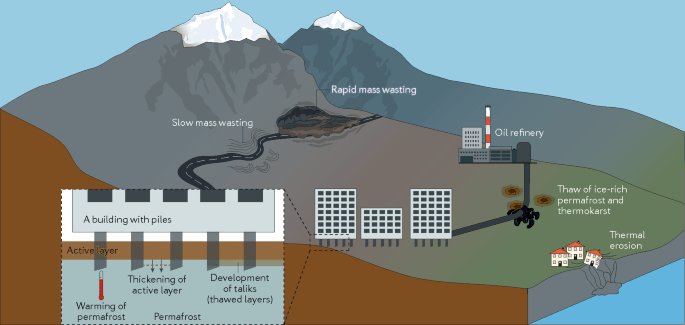
Climate Change and Permafrost thawing
As climate change or warms, the ice inside the permafrost melts (thawing). Thawing causes several adverse effects:
- People have built habitations over permafrost soils. As permafrost thaws, habitations and infrastructure would be collapsed.
- The surface layer above the permafrost soils contains large quantities of organic carbon. Due to severe cold, bacteria cannot decompose (for want of heat) the biomass or material leftover from dead plants. Once permafrost thaws with global warming, microbes begin the process of decomposing this material, which releases greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and methane to the atmosphere.
- Scientists say as permafrost thaws, so are the ancient microbes (bacteria and viruses), and then the unfrozen microbes can be harmful to human and animals health.
- Environmental scientists attributed the Nanda Devi glacial melt to global warming or climate change.
- Glacier retreat and thaw are expected to decrease the stability of the mountain slopes and increase the number and area of glacier lakes.
Need to reverse Climate Change
Thus, permafrost thawing has become a global problem and the scientists are closely monitoring Earth’s permafrost through satellite observations.
They estimated that for every 1 degree Celsius rise in temperature, these permafrost grounds could release GHGs equivalent to the tune of 4-6 years of emissions from coal, oil, and natural gas.
–
Melting of Himalayan Glaciers
The Hindu Kush Himalayan (HKH) region is 3,500 km long spread over eight countries in South Asia and home to 10 major river basins and 4 biodiversity hotspots, is under severe threat of climate change. The HKH region acts as a heat sink in summer and heat source in winter.
The HKH region forms the largest area of permanent ice cover (glaciers) outside of the North and South Poles. Hence it is often called the “Third Pole”.
However, global warming resulted in the melting of Himalayan glaciers in the region. The Hindu Kush Himalaya Assessment Report revealed that more than 35 % of the glaciers in the region could retreat by 2100, even if the global temperature rise is capped at 1.5º C.
Reasons for Glacial Melting
- Climate change is the cause of glacial melting. Greenhouse gases emission and resultant rising temperature is the major cause of climate change.
- Elevation Dependent Warming-temperatures are warming faster than the global average at high elevation regions (mountains).
Effects of Himalayan Glacial Melting
- Melting of glacial results in Glacial Outburst. Sudden glacial outburst destroys habitats and infrastructure. Recent Uttarakhand Glacial outburst washed away at least two hydroelectric power projects– Rishiganga Hydro-electric power project and Tapovanam project- and killed many people.
- Thawing of Permafrost
- The intensity of extreme precipitation has increased overall in the last five decades have recorded.
- Potentially threatening the water supply for hundreds of millions of people in countries in the region.
- Increases probability of Landslides.
- Pose threat to the hotspots has a rich variety of gene pools, species, and global importance, many of which are found only in the region.
Way Forward
- Scientific evidence calls for concerted and urgent climate action with immediate conservation efforts to safeguard the region and meet the Paris Agreement emission targets.
Also Read –
.
Read More Articles on Geography
You Can Follow on Youtube – Score Better
Join Us on Telegram For More Update
.
[…] Permafrost and Adverse Effects […]