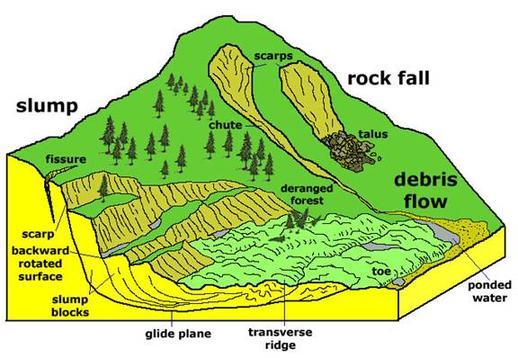
Over 420,000 sq. km., i.e. nearly 12.6%, of India’s land, is prone to landslides (excluding snow-covered areas). According to the 2018 India Spend report, which examined more than 5,000 landslides between 2004 and 2016, India registered the most deaths (10,900 deaths across 829 landslides) in the world caused by human-triggered landslides.
This is equivalent to 18% of the world’s landslide casualties over those 12 years. During this time period, India also accounted for a maximum (12% of the total) of mining-triggered landslides worldwide.

Landslides: Disaster Risk Reduction Measures
- National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) issued guidelines for Landslides.
- National Remote Sensing Center (NRSC), Department of Science and Technology (DST) in collaboration with various universities have developed Atlas for assisting the development of landslide mitigation strategies.
- GSI is the nodal agency for landslide studies:
- Coordinating geological studies for landslide hazard mitigation
- Carrying out landslide hazard zonation
- Monitoring landslides and avalanches and
- Studying the factors responsible for land sliding and suggest precautionary measures
- National Core Group for Landslide Hazard Mitigation has finalized the action plan for landslide studies with inputs of GSI and other organization. The action plan includes:
- Monitoring landslide hazard zonation
- Monitoring impact of landslides
- Uniform methodologies for LHM
- Carrying out Landslide Hazard Zonation of vulnerable areas on macro scales and identified areas on meso scales
- Evolving an Early Warning System
- Preparing Inventory/ Database on Landslide Hazard Zonation
- Advising the state governments various aspects of landslide hazard mitigation
Ways and means to protect individuals from landslide-related deaths include:
- Early warning systems and proactive or pre-planned landslide action policies to mitigate damage.
- Putting in place building laws considering the specific ecological constraints in the region and then regulating construction plans.
Issues in Landslide Risk Reduction Measures
- India’s micro-level land development regulations do not consider ecological diversity.
- A 2019 National Institute of Disaster Management report and IndiaSpend reports that a 2014 study and flag that land development regulations applied in hilly towns are inspired by city-based master plans, and do not take a hilly region’s topography, hazard potential, and socio-developmental context into consideration.
- As per the study of NIDM report, In the micro-level, the Urban Local Bodies (ULBs) of Indian Himalayan Region (IHR) and Western Ghats (WG) States are either not having local land use planning or if they have, it not being updated. It is resulting in ill-conceived planning, unplanned development, and ultimately slope instability.
- The recent Environment Impact Assessment (EIA) has been criticised for prioritizing ease of doing business and development over environmental justice, which would further endanger ecologically sensitive regions and the people living in them.
Way Forward
- Regular updating of the inventory of landslide.
- Landslide hazard zonation mapping in micro, meso and macro after consultation with the all the stakeholders including Border Road Organization, State government and local communities.
- The government should ensure a balance between environment and development.
.
Read More Articles on Geography
You Can Follow on Youtube – Score Better
Join Us on Telegram For More Update
.